Smart Agriculture

Smart agriculture is transforming traditional farming by using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and coding to automate irrigation and fertilization. With rising concerns about climate change and resource scarcity, this tech-driven approach helps optimize water and nutrient use, improve yields, and reduce manual labor.
A modern smart agriculture system includes soil sensors, storage tanks for water and essential minerals like Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K), and a central control system that automates decisions. These soil sensors detect moisture and mineral levels and send real-time data to a microcontroller. Based on coded AI algorithms, the system determines when and how much water or nutrients to release from the tanks—self-irrigating the crop fields without human involvement.
Table: Traditional Farming vs Smart Agriculture
Features | Traditional Farming | Smart Agriculture (AI-Based) |
Irrigation | Manual or scheduled | Automated, sensor-based |
Nutrient Application | Estimated manually | Precise, data-driven dosing |
Water Usage | Often excessive | Efficient and controlled |
Field Monitoring | Visual/manual checks | Real-time digital tracking |
Decision Making | Human intuition | AI and data-powered |
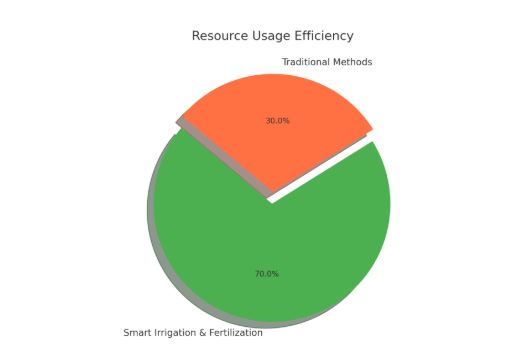
Pie Chart: Resource Usage Efficiency
A clear comparison of how efficiently resources are used:
l Smart Irrigation & Fertilization – 70%
l Traditional Methods – 30%
Graph: Crop Yield Over Time
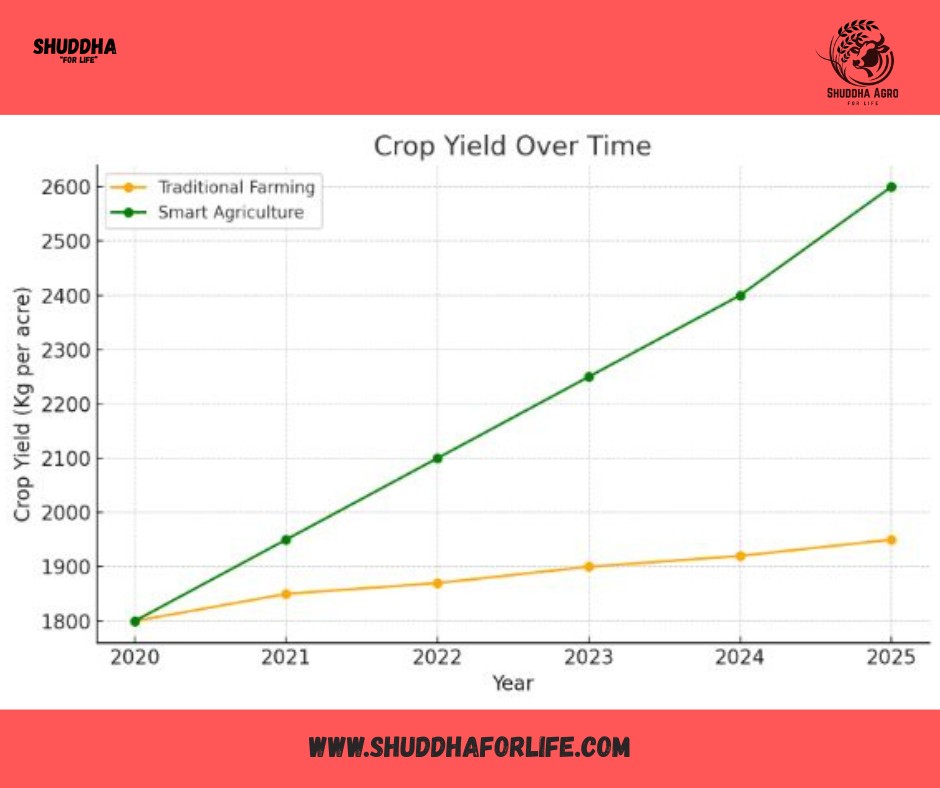
Smart farming steadily outperforms traditional methods.
Conclusion
Technology is rapidly reshaping farming. With AI and coding, we now see crops irrigated and nourished at the right time with precision. These systems save water, boost yields, and reduce waste. As we look ahead, air (drones) and tech (AI, IoT) will define the future of farming—bringing innovation from soil to sky.
Related Posts

12 Aug, 2025
Why Beginners Fail in Agriculture and Cattle Farming in Nepal
an article to show attraction practices and failure reasons
 HOME
HOME